Slug
What is a slug in WordPress?
In WordPress, the “slug” refers to the part of a web page’s address that appears after the domain name.
A slug is a smaller piece or component of something larger.
URL or Uniform Resource Locator is a string of characters that specifies where a resource is on the internet.
Browser using DNS servers translates URL to the specific IP address, and then the server returns a particular resource based on the entire URL, including HTTP protocol.
A simple WordPress slug example would be if you visited a page at www.example.com/about-us/, then:
URL is: www.example.com/about-us/
slug is: about-us
The slug is the part of your URL that you can edit (change) when writing a new post. This is how to edit the slug in WordPress (old editor):
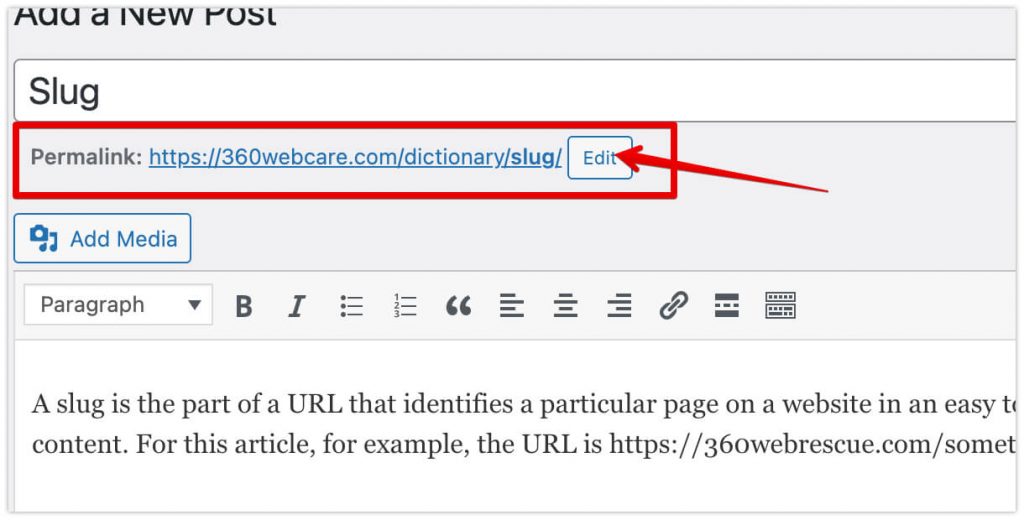
NOTE: This only works with the right permalink settings. You can edit the permalink settings in WordPress through Settings > Permalinks.
Slugs are typically short, human-readable strings that can be easily read and understood. They are also lowercase and use dashes (-) instead of spaces to separate words.
Slugs are used in WordPress permalinks to define which content is being requested. WordPress uses them throughout the WordPress codebase and templating system to refer to specific objects (such as posts, pages, categories, etc.).
A good slug can improve the user experience on your website and help with SEO.
We use slugs to create unique and clean URLs for your content. They can help improve your website’s SEO by making your links more keyword rich. Additionally, slugs can make it easier for people to share your content on social media as they are typically shorter and more accessible to remember than a long URL.
How to edit WordPress slugs?
To edit a slug in WordPress, go to the post or page section and click on the “Edit” link next to the post or page you want to change. In Gutenberg editor, you can find it on the right sidebar in the “Post” or “Page” Toolbar.
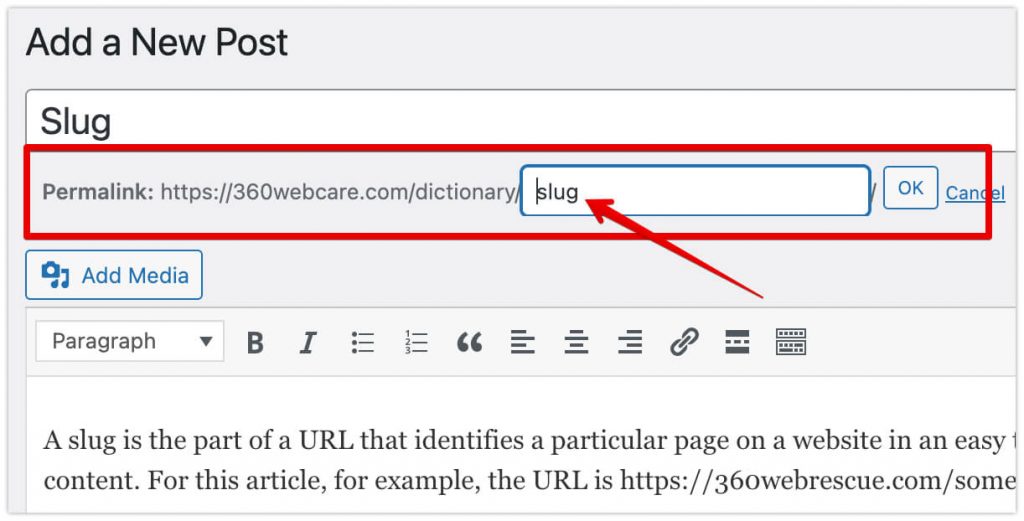
On the Edit screen, scroll down to the Permalink section and click on the “Edit” button.
If you’re creating a new WordPress post or page, you can set the slug in the permalink field, which is located just below the title field. You can edit the slug for existing content by clicking on the “Edit” link next to the permalink.
If you don’t enter a custom slug, the WordPress slug generator can create a slug automatically based on the title of your post or page. It will allow you to edit the slug for that specific post or page. However, you can also edit the slug manually to improve readability or for SEO purposes.
It’s important to note that once you create a slug for a piece of content, you cannot change it without creating a new URL. Therefore, it’s essential to choose your slug carefully before publishing!
Changing a slug after saving to the database can cause problems with permalinks and links to other content on your site. It generates a 404 error when someone clicks on the “old” slug to visit your website. It is an excellent practice to create 301 redirections of an old URL/slugs to new ones.
When editing slugs, it is essential to keep a few things in mind:
- slugs should be short and descriptive
- slugs should be relevant to the content
- slugs should use lowercase letters, numbers, and hyphens
- slugs should not include special characters
- slugs should not be too long
- use only ASCII characters.
Following these guidelines will help ensure that your slugs are SEO-friendly and user-friendly.
How to best optimise your URL/slug for SEO?
1. Keep it short and sweet – A slug should be no longer than 6-8 words
2. Use keywords – A slug should include 1-2 of your target keywords for the page/post
3. Avoid stop words – Stop words are common words that offer little value to the reader or search engines, such as “a”, “the”, “of”, etc. It’s best to avoid using these in your slug as they add unnecessary length without contributing anything valuable.
4. Use hyphens to separate words – This makes your slug easier to read and understand for both humans and search engines.
5. Make it unique – Every slug on your site should be unique to avoid confusion for users and search engines. Duplicate content can hurt your SEO, so making sure each slug is original is essential.
How long should a slug be?
A slug should be as short as possible while still being descriptive. A good rule of thumb is to keep your slug no more than 3-5 words long and under 60 characters. It will ensure that it works well with most web servers and browsers and fits within Google’s recommended length for a URL.
What characters should I use in a slug?
You should use lowercase letters, numbers, and hyphens in your slug. You should avoid using special characters or spaces as they can cause problems with some web browsers.
What if I have a lengthy title?
If you have a long title, you can try editing it to make it shorter or using a slug generator to create a slug automatically.
Why should you use dashes except for other separators in the slug?
Browsers use slugs in URLs, and URLs can not contain spaces. That’s why using dashes as separators is a good practice.
Different slug separators are treated differently by different servers and web browsers. Dashes tend to work most consistently across different setups. Additionally, Google prefers dashes (hyphens) over other slug separators. Google views URL dashes (hyphens) as word separators, while an underscore in your slug for the browser is as one long word. Google cuts off this type of slug in the SERP (Search Engine Result Page), which is not ideal.
Following these tips can help you create a compelling and SEO-friendly slug!