The Cost of Website Downtime

Website downtime is never welcome for any business. The average cost of downtime is $5,600 per minute, which extrapolates to well over $300K per hour, according to a 2014 study by Gartner. Downtime can be costly for companies of all sizes. The good news is that there are ways to reduce the downtime your website can experience. In this blog post, we will discuss the cost of website downtime and how you can take steps to minimize it. We will also look at real-world examples of how downtime can negatively impact a business.
Key takeaways
- Website downtime is a global problem, and it generates mass losses.
- You can prevent website downtime by limiting factors causing downtime
- Recovery from downtime will be much faster when the company is prepared and have a plan
- You can outsource website management to industry experts.
Table of contents:
Table of Contents
- Key takeaways
- What is website downtime?
- What causes website downtime?
- What is the impact of website downtime on the business?
- How do you calculate downtime costs?
- Is website downtime a real problem?
- How can I prevent website downtime?
- Steps businesses can take to reduce downtime
- Prepare a website rescue plan.
- Set up uptime monitoring
- Set up a downtime page
- Handle the problem on social media and support.
- Choose a good-quality hosting provider.
- Secure your website.
- Optimize the website performance.
- Renew the domain name on time.
- Use maintenance services.
- Is website downtime a real problem?
Last update 05-08-2022

What is website downtime?
Website downtime occurs when a website is unavailable online or not functioning correctly. Many factors can cause downtime, including server issues, website crashes, or maintenance. Downtime can also occur if there is an issue with your website’s domain or hosting. Nowadays, downtime is more complex than we believed it was a few years ago, and even websites with long response times can be considered down.
We can consider slow websites with poor Core Web Vitals results inaccessible because nobody wants to wait 10 seconds for the FCP (see: First Contentful Paint). In the same way, a website without proper cross-device performance can also be considered non-accessible. Downtime is subjective, and it is easy to define it as the state opposite of website uptime.
When we think about downtime, we always have two essential things in mind:
- time – how long the website is down, in seconds, minutes, hours, days etc., time is a base to calculate the cost of downtime,
- what constitutes downtime – currently, this is more complicated than obvious 5XX error or general website failure, and it is a crucial factor in terms of recovery from downtime
What causes website downtime?
Several factors can contribute to downtime. Common causes include server issues, website crashes, domain name problems, and hosting issues.
- human error – e.g. wrong DNS entry on the server, error in PHP causing disconnection with database
- hardware failure – e.g. server or network breakdown, power outage and any other reason caused by the hardware failure
- malicious attack – e.g. malware infection, Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attack, DNS (Domain Name Servers) cache poisoning, hijacking or redirection, any other malicious activity causing downtime
- catastrophic accident and natural disaster – e.g. fire in the server room (read about this in our article “Fire in the server room – why do you need independent backup “)
- massive traffic, which creates server overload – even success can bring failure. If you expect huge traffic, check that your server can handle it.
- expiration of the domain subscription (renewal of a domain name at the registrar)

What is the impact of website downtime on the business?
Website downtime can have several negative impacts on businesses. First, it can lead to lost sales and revenue. Customers cannot purchase products or services from your website if it is down. Additionally, downtime can also damage your business’s reputation. Customers may perceive your business as unreliable if your website is frequently down.
What are the immediate effects of downtime?
- the website becomes unavailable to customers
- lost sales and revenue
- lose potential customers
- damaged reputation
What are the potential losses of downtime?
Potential short-term losses:
- Customers cannot purchase products or services.
- The website may receive negative reviews.
- The potential loss of regular users
- Loss of an advertising revenue
- Increase customer support costs
Potential long-term losses:
- Outages can impact SEO, and the website may rank lower on search engine rankings.
- Businesses may lose out on new customers who visit the website during the downtime.
- The company can lose its reputation.
- Some users will never return, and downtime increases permanent site abandonment.
What are the additional costs of website downtime?
Additional costs associated with downtime include lost productivity, advertising revenue, and customer support costs. Additionally, website downtime can also lead to data loss.
Additional costs:
- Recovery costs
- Productivity loss
- Data loss
- Service delivery interruption costs and compensations for users, e.g., selling SAAS solutions (Software As A Service), depends on agreements.
- damage to physical equipment
The cost of downtime can vary. It depends on several factors, including the size of your business and the length of time your website is down. However, it’s safe to say that website downtime can cost companies a lot of money. One study found that the average cost of website downtime is $5600 per minute!
How do you calculate downtime costs?
There are a few different ways to calculate the cost of downtime. One method is to look at your business’s monthly revenue and multiply it by the percentage of time your website is down. For example, if your website is down for two hours and your monthly revenue is $100,000, your website downtime would cost your business $500.
Another method is to use the “cost per minute” method. It involves multiplying the average downtime cost by the length of time your website is down. For example, if your website is down for one hour and the average cost of website downtime is $5600, the total cost of website downtime would be $5600.
Quantifying the impact of downtime:
- Evaluating downtime losses
- Calculating the cost of website downtime based on a benchmark
- Calculating the loss based on uptime percentages
- Downtime revenue losses basic formula
For example, the formula for gross revenue loss in a situation when the website is fully inaccessible will be:
L = (GR/T) x TD
in this formula:
- L – total loss of Gross Revenue
- GR – Gross Revenue
- T – time for the Gross Revenue period, e.g. one month, one year
- TD – Total Downtime
Always use the same time measure for T and TD, for example, [seconds
Example calculation: let’s say that the monthly (T) gross revenue (GR) for the international e-commerce company is $200,000, and the website experienced downtime (DT) for two days.
GR = $200,000
T = 1 month = 30 days x 24 hours x 60 minutes x 60 seconds = 2,592,000 secondsseconds
TD = 2 days = 2 days x 24 hours x 60 minutes x 60 seconds = 172,800 seconds
L = ($200,000/2,592,000 sec) x 172,800 sec = $13,333.33
In this example, we simplified many essential factors, for example:
- E-commerce sites usually run sales for limited hours (e.g. 10 h/day). It can impact the result when downtime happens during peak sales time.
- Sales usually fluctuate during the week/month/year.
- We haven’t calculated additional costs like recovery costs, data-loss costs etc.
- We didn’t consider potential losses like permanent site abandonment, SEO page ranking drop, and brand credibility loss.
Is website downtime a real problem?
Yes, it is a real problem, and businesses must be aware of it. As we’ve seen, downtime can cost companies a lot of money in lost sales and revenue. Additionally, downtime can damage your business’s reputation. Therefore, it is crucial to take steps to reduce the amount of website downtime your business experiences.
Amazon could have lost anywhere from $72.4 million to $99 million in missed sales during the hour the site was down during Prime Day.
How can I prevent website downtime?
Site downtime can be costly for businesses of all sizes. However, there are steps you can take to reduce the amount of downtime your website experiences. By taking these steps, you can help minimize the impact of downtime on your business.
Steps businesses can take to reduce downtime
- Prepare a website rescue plan,
- Set up uptime monitoring service
- Make regular backups in multiple locations.
- Choose a good-quality hosting provider.
- Secure your website thoroughly, and employ advanced security features.
- Install DDoS attack (Distributed Denial of Service) protection.
- Optimize the website’s speed, loading time (you can use free tools), and response time.
- Renew the domain name on time.
- Use a dedicated server or VPS to improve website availability.
- Make sure your DNS hosting works well, and prepare a backup DNS hosting server (different provider).
- Secure with care all sensitive data kept on the server.
- Set up a downtime page.
- Handle the problem on social media
Prepare a website rescue plan.
The website rescue plan should include a list of steps during the site’s downtime. Design the plan to help minimize the impact of downtime on your business.
The plan should include:
- risk identifications
- possible solutions for recovery (spare web server, backups, procedures)
- human resources responsible for the plan execution
- media and public relations management

Set up uptime monitoring
An uptime monitoring service is checking whether a website or system is operational. There are many different uptime monitors available, both paid and free. Some examples of website monitoring service providers:
- Pingdom
- New Relic
- Site24x
- Uptime Robot
- Uptime.com
- Uptrends
Set up a downtime page
A downtime page is a special page displayed when a website is down. This page should include the downtime of the site and how long it is expected to last. Additionally, this page can provide alternative ways for customers to contact your business or access your services, e.g. phone or helpdesk support or even social media. Additionally, keep the website support team updated on the website status (downtime) and when it is expected to be resolved.
Handle the problem on social media and support.
During downtime, it is vital to keep your customers informed. Social media and support are two ways you can do this. Regularly check for mentions of your business on media. If there are negative comments, respond and apologize.
On website support, check for downtime-related issues and assist customers as needed. Additionally, keep the website support team updated on the status of website downtime and the expected time, and other detailed information on the problem will resolve.
Choose a good-quality hosting provider.
The quality of the hosting provider can have a significant impact on website downtime. On a shared hosting plan, your site shares resources with others on the same server.
It can lead to problems if another site on the shared server uses too many resources, causing your website to go down. These are common problems of shared hosting services so consider moving to a virtual personal server or dedicated server and to the centre with a high-speed internet connection.

Secure your website.
Website security is essential to prevent website downtime. There are many ways to secure your website, including:
- hardening the website
- using a secure password for your website
- using two-factor authentication (2FA)
- keeping your WordPress website up-to-date
- backing up your site regularly
- To prevent DDoS attacks, use a firewall
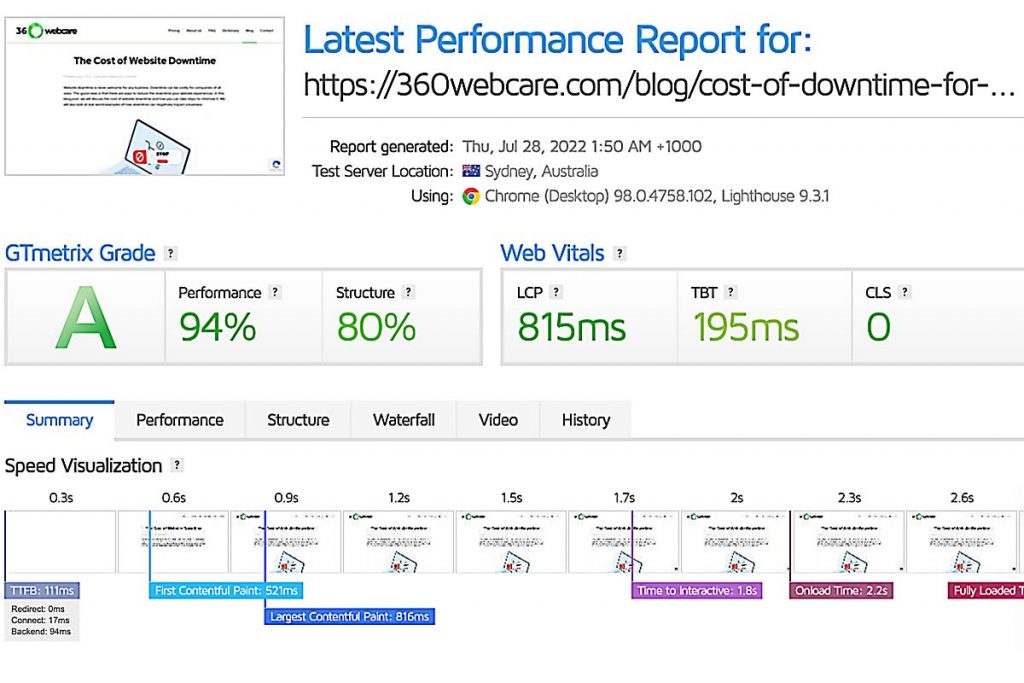
Optimize the website performance.
Website speed is vital for website uptime. A slow site can lead to crashes and downtime. A website’s speed can impact search engine optimization (SEO) and ranking.
There are many ways to optimize speed, including:
- optimizing site code
- compressing images
- using a caching plugin
- using a content delivery network (CDN) for the international pages
- minimize the use of external scripts.
Renew the domain name on time.
Domain expiry is a common cause of downtime. If your domain expires, your site will go offline. To prevent this, renew your domain at your registrar on time. Additionally, you can set up auto-renewal for your domain to ensure it does not expire.
Use maintenance services.
WordPress requires regular care and maintenance to function correctly. Choose a good site care plan with a service level agreement in place. Keep your content management system and plugins up-to-date and secured.
Is website downtime a real problem?
Yes, website downtime is a real problem that can cost businesses money. Downtime can occur for various reasons, including server overload, power outages, and cyber-attacks. Site outages can lead to lost revenue, increased costs, and damaged reputations. Therefore, businesses need to take steps to reduce downtime.
According to the news provider Axios,” Amazon could have lost anywhere from $72.4 million to $99 million in missed sales during the hour the site was down during Prime Day, analysts are estimating.” Digital Commerce 360 estimates the downtime costs Amazon $US72 million, while Love the Sales’ Liam Solomon estimates it costs Amazon up to $US99 million.
Amazon reported revenues of $386 billion in 2020, which gives us an average of $734,398 every minute in today’s numbers, or a $9,547,184 cost if the 13-minute episode from 2016 would happen in 2020.
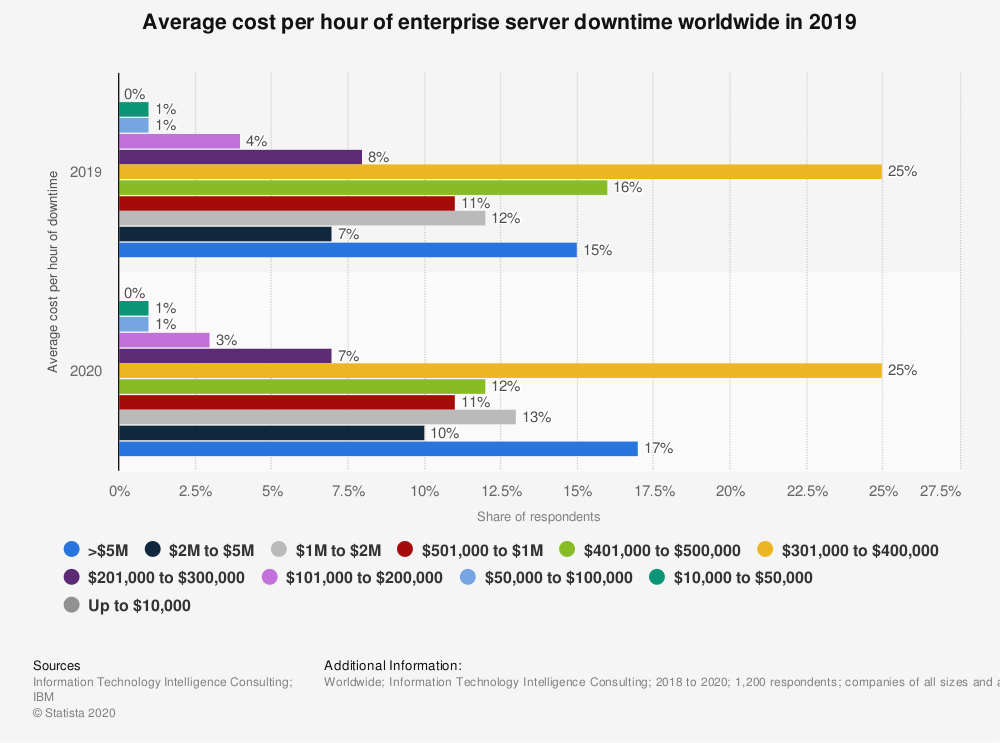
According to IBM, in 2020, responders reported an average cost per hour of the enterprise server downtime cost between:
- $301,00 to $400,00 – 25%
- >$5M – 17%
Complete results data in the graph below.
Website downtime can cost businesses money in lost sales and revenue. Additionally, site downtime can damage your business’s reputation.
Summary
Downtime is challenging to avoid, but suitable support systems and monitoring solutions can reduce it to near zero.
This is the reason why you should just be prepared. Having the proper resources and plan can ensure you recover quickly without more significant problems.
This will keep you from losing revenue, but it will improve the overall impression you make with users and potential customers.